Java Decompiler
A Java decompiler is a reverse engineering tool that can be used to convert Java bytecode back to Java source code. It became useful when we had the compiled Java classes (in the form of bytecode, typically stored in a.class file) but not the original source code. In this tutorial, we will learn how we can convert Java class file to source code.
Java Decompilers Example
There are several Java decompilers available; the following are some of the well-known Java decompilers:
- JD-GUI (Java Decompiler Graphical User Interface):
- Website: http://jd.benow.ca/
- JD-GUI is a standalone graphical utility that displays Java source codes of “.class” files.
- Procyon:
- GitHub Repository: https://bitbucket.org/mstrobel/procyon
- Procyon is an open-source Java decompiler that supports Java 5 and later.
- Fernflower:
- GitHub Repository: https://github.com/fesh0r/fernflower
- Fernflower is another open-source Java decompiler. It is part of the IntelliJ IDEA community edition.
- Bytecode Viewer:
- GitHub Repository: https://github.com/Konloch/bytecode-viewer
- Bytecode Viewer is a Java decompiler that includes a built-in editor for bytecode and other features.
Decompilation Process
- Java decompilers take the Java bytecode as the input.
- It analyses the byte code and attempts to construct the Java source code.
- The resulting source code generated by the Java decompilers may not be identical to the original source code, as some of the information may be lost during the compilation process.
How to Convert .java file to .class file?
We are going to use the Java JAD decompiler to convert the Java class file to a Java source code file.
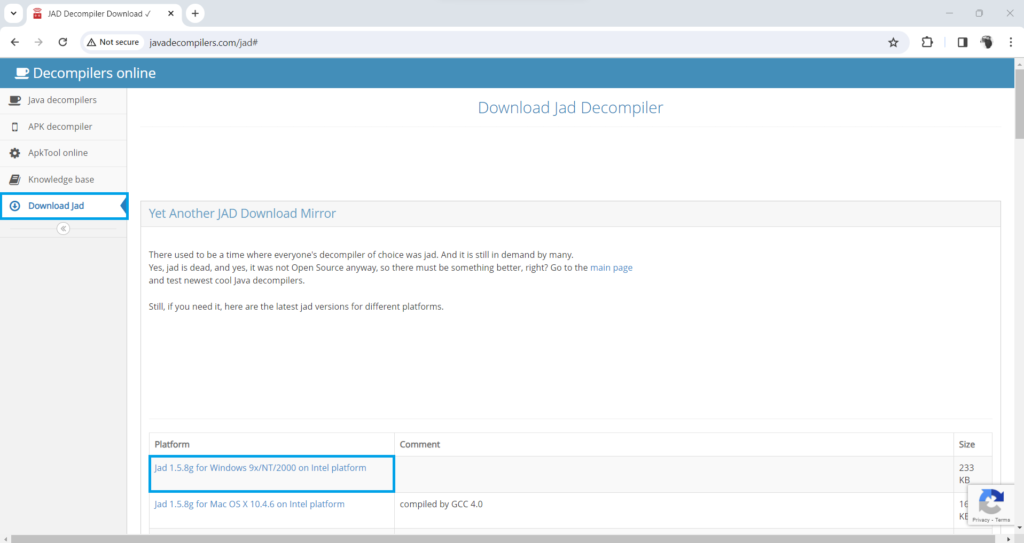
Step 1- Download Java decompiler – Java JAD
First, we need to download the Java JAD decompiler. Make sure to download the JAD corresponding to the operating system. Here, we are downloading it for Windows.
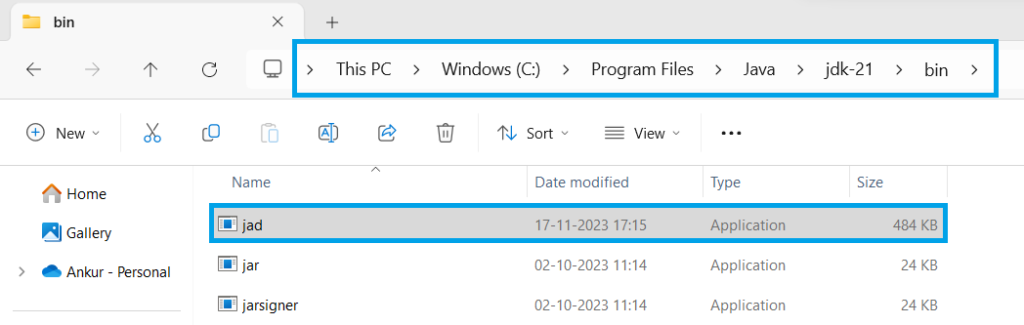
Step 2- Java JAD Path
After we have downloaded the JAD, we need to extract it and place (copy) it inside the bin directory of our Java application. Make sure to place it inside the bin directory of the Java version that is currently setup on the computer. Here, we are placing it inside Java 21, as currently this version is being setup in our system.
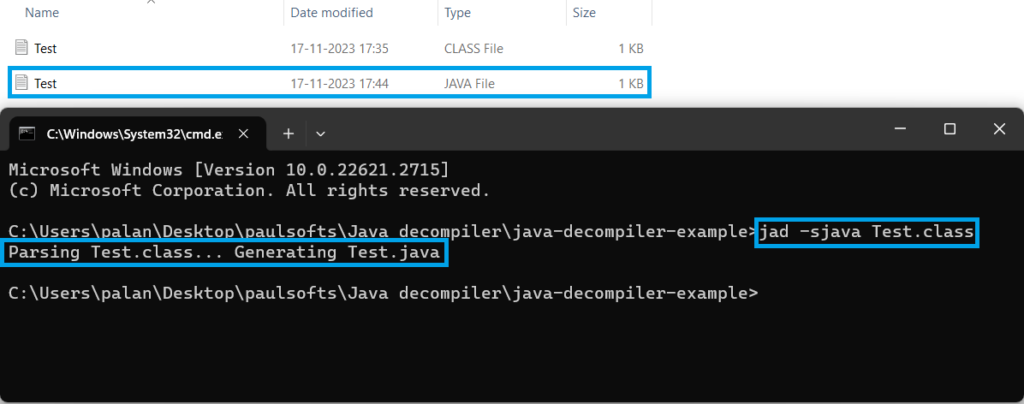
Step 3- Testing the Decompiler
As we can see, we have a Test.class file that contains bytecode. We will open the command prompt at the location where our class file is present and run the following command to convert this.class file to a.java file:
jad -sjava Test.classThis will generate our source file. i.e, Test.java.
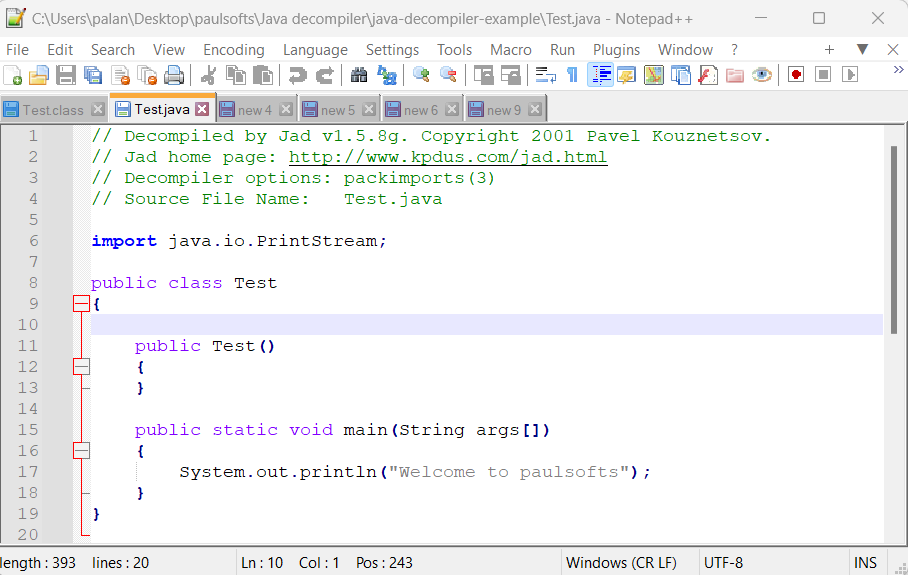
As we can see below, it has generated the Test.java class.