On May 5, 2020, the auto-incrementing ID column in a shared database table on Github grew larger than what the MySQL integer type could handle. The github-blog page has all of the incident’s information. We will simulate the situation in which we force the value of our auto-increment ID column in the MySQL database to reach its maximum value in our local environment.
Auto-increment ID column reaches its maximum value
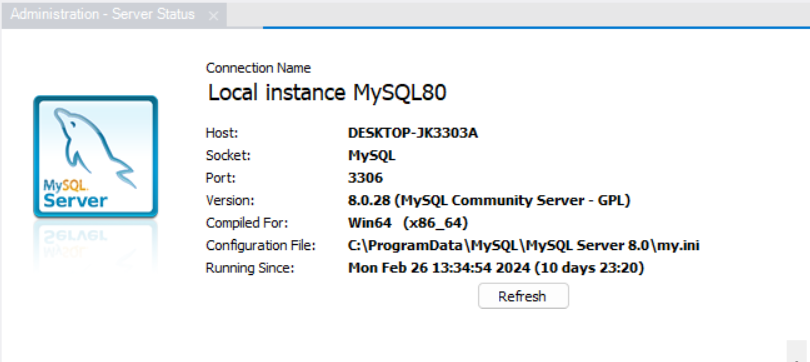
We will be using MySQL Workbench with MySQL 8.0.28 in this example.
Step 1- Create DB schema
We start by building a database schema. To find out, please visit MySQL Workbench – How to make database schema in MySQL Workbench?.
Step 2- Create Table in MySQL
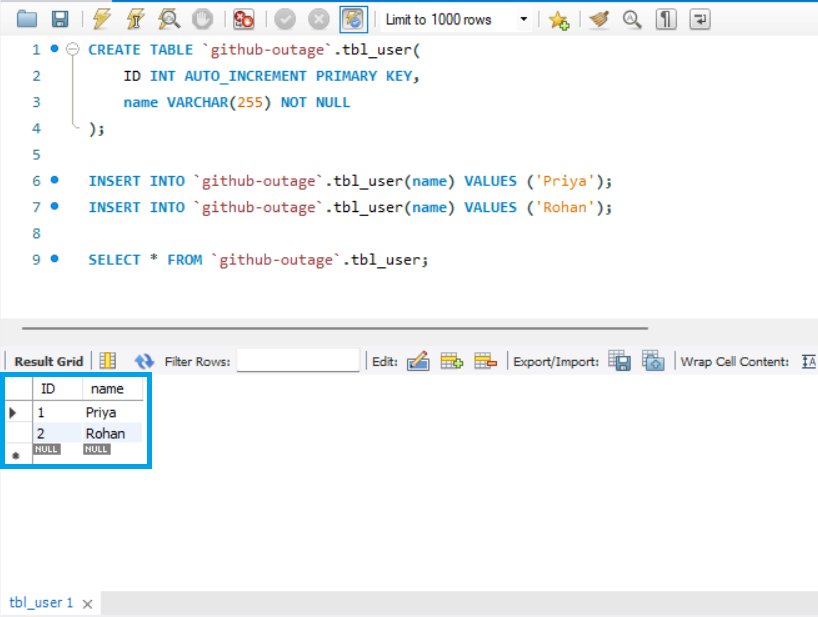
We make a table called tbl_user with an ID column and a name. Our primary key will be the ID column, which will automatically increment.
CREATE TABLE `github-outage`.tbl_user(
ID INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL
);Step 3- Integer Maximum Value
Below, we’ll see the highest integer value that MySQL 8.0 supports.
| Type | Storage (Bytes) | Minimum Value Signed | Minimum Value Unsigned | Maximum Value Signed | Maximum Value Unsigned |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
TINYINT | 1 | -128 | 0 | 127 | 255 |
SMALLINT | 2 | -32768 | 0 | 32767 | 65535 |
MEDIUMINT | 3 | -8388608 | 0 | 8388607 | 16777215 |
INT | 4 | -2147483648 | 0 | 2147483647 | 4294967295 |
BIGINT | 8 | -263 | 0 | 263-1 | 264-1 |
Above, we can find that the integer value starts from -2147483648 ( 231) to 2147483647 (231-1).
Step 4- Add data to the table
We will now update the table with data. We’ll use the following query for this.
INSERT INTO `github-outage`.tbl_user(name) VALUES ('Priya');
INSERT INTO `github-outage`.tbl_user(name) VALUES ('Rohan');The above command will add two rows with the name and auto_increment ID column to tbl_user.
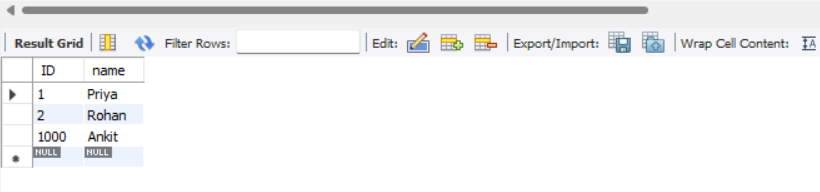
We now explore a little bit with the data ingestion section. Assume that the ID column is explicitly specified in the INSERT statement.
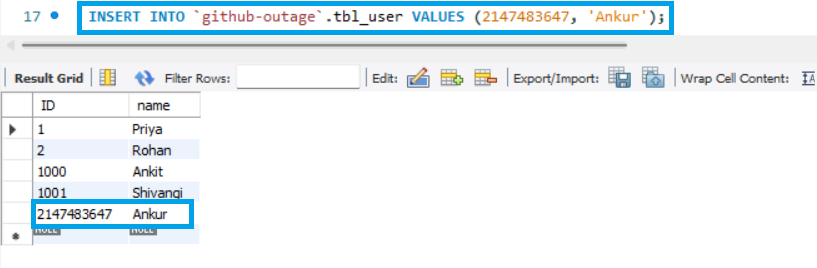
INSERT INTO `github-outage`.tbl_user VALUES (1000, 'Ankit');As we have specified the ID column explicitly, it will insert the data with the specified ID.
If we attempt to insert again without naming the ID column, auto_increment will cause data to be inserted into tbl_user with the ID set to 1001, increasing the value of the previous ID column.
It indicates that the maximum value supplied is used to replace the internal auto_increment offset.
Step 5- Add maximum possible int value
We will attempt to input the largest integer value that MySQL can support, that’s 2147483647.
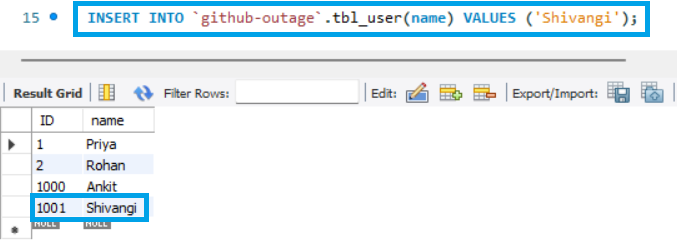
Now, we will insert one more statement, and it will be auto-incremented, pass over the maximum value, which is supported by an integer, and observe the behavior of MySQL. We will be using the following query:
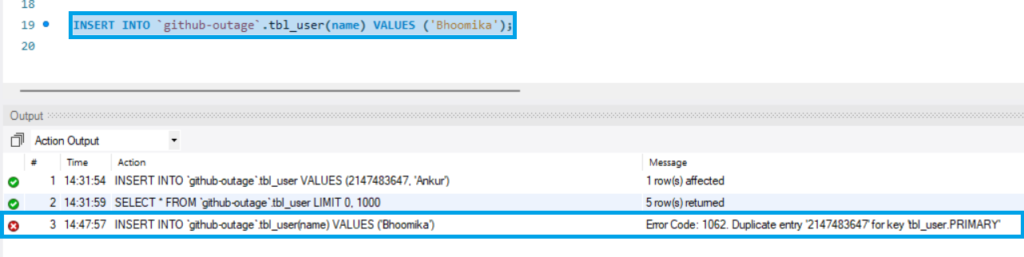
INSERT INTO `github-outage`.tbl_user(name) VALUES ('Bhoomika');MySQL is displaying an error message indicating a duplicate item below. Instead of a duplicate entry, which is obviously not the case, it should be more generic and provide context for the error.